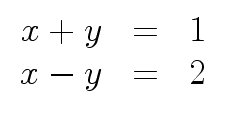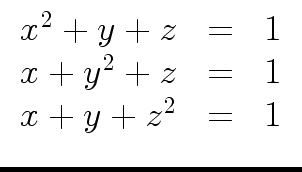

Next: A breif history
Up: Computer Algebra
Previous: Computer Algebra
Computer algebra is the set of the techniques for performing
algebraic calculations on computers. This includes developing
- algorithms and data structures for these calculations,
- programming languages and software systems implementing them,
- interfaces between computer algebra systems.
By algebraic calculations we mean symbolic or exact computations.
- Most of the calculations that we have learned at school were of that kind.
For instance we have learned
- to solve equations of the form
ax2 + bx + c = 0
mathend000#,
- to factor such polynomials,
- to decide whether a number is prime,
- to solve systems of linear equations such as
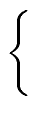
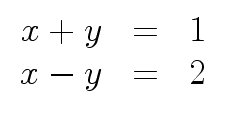 mathend000#.
mathend000#.
- Most of the calculations that scientific calculators are not of that kind.
For instance, these calculators
- give approximate solutions of
x2 + x - 1 = 0
mathend000#,
- sometimes factor polynomials of low degree,
- rarely do primality test,
- give approximate solutions of linear equations of small order.
Actually, these high-school problems are not that easy:
- solving equations of the form
ax5 + bx4 + cx3 + dx2 + ex + f = 0
mathend000#,
- factoring univariate polynomials, such as
x4 +2x3 +4x2 + 2x + 3
mathend000#,
- deciding whether a number is prime,
- solving systems of linear equations of high order.
Several kinds of difficulties appear there:
- for some problems, we do not know a practical algorithm, or
the algorithms that we know are too greedy
in time or space,
- for other problems, we may not even know an algorithm to compute the solution.
Computer algebra aims at remedying these difficulties, as much as possible.
Let us illustrate the question of exactness with an example.
Consider the following system of 3 non-linear equations
in 3 variable:
The output with phc the symb.-num. software
of J. Verschelde (Univ. Chicago):
solution 1 : start residual : 3.968E-12 #iterations : 1 success
x : 9.99999695984909E-01 4.13938269379988E-07
y : 3.04015091103714E-07 -4.13938269379988E-07
z : 3.04015090976779E-07 -4.13938269379988E-07
== err : 2.154E-06 = rco : 1.197E-07 = res : 9.920E-13 = complex regular ==
solution 2 : start residual : 1.388E-16 #iterations : 1 success
x : 4.14213562373095E-01 2.35098870164458E-38
y : 4.14213562373095E-01 -1.67507944992176E-37
z : 4.14213562373095E-01 1.29304378590452E-37
== err : 7.517E-16 = rco : 6.017E-02 = res : 5.551E-17 = real regular ==
solution 3 : start residual : 2.400E-12 #iterations : 1 success
x : 1.80048038888678E-08 4.29782537417684E-07
y : 9.99999981995196E-01 -4.29782537417684E-07
z : 1.80048038262633E-08 4.29782537417684E-07
== err : 1.344E-06 = rco : 7.463E-08 = res : 5.995E-13 = complex regular ==
solution 4 : start residual : 9.614E-13 #iterations : 1 success
x : 1.00000024904061E+00 -3.93267692590196E-08
y : -2.49040612161639E-07 3.93267692590197E-08
z : -2.49040612108234E-07 3.93267692590197E-08
== err : 8.657E-07 = rco : 4.806E-08 = res : 2.400E-13 = complex regular ==
solution 5 : start residual : 2.745E-12 #iterations : 1 success
x : 3.58839953269127E-07 1.89357516639334E-07
y : 3.58839953269127E-07 1.89357516639334E-07
z : 9.99999641160047E-01 -1.89357516639334E-07
== err : 1.645E-06 = rco : 7.071E-08 = res : 6.863E-13 = complex regular ==
solution 6 : start residual : 1.744E-34 #iterations : 1 success
x : -2.41421356237309E+00 0.00000000000000E+00
y : -2.41421356237309E+00 0.00000000000000E+00
z : -2.41421356237309E+00 -1.00577224408752E-106
== err : 3.611E-35 = rco : 4.142E-01 = res : 6.868E-106 = real regular ==
solution 7 : start residual : 1.112E-12 #iterations : 1 success
x : -2.64786238552867E-07 -4.67724648385200E-08
y : -2.64786238552867E-07 -4.67724648385200E-08
z : 1.00000026478624E+00 4.67724648385200E-08
== err : 9.341E-07 = rco : 4.530E-08 = res : 2.779E-13 = complex regular ==
solution 8 : start residual : 2.045E-12 #iterations : 1 success
x : 1.42636460554469E-07 -3.16738323586431E-07
y : 9.99999857363539E-01 3.16738323586431E-07
z : 1.42636460467758E-07 -3.16738323586431E-07
== err : 1.378E-06 = rco : 7.656E-08 = res : 5.117E-13 = complex regular ==
===========================================================================
A list of 8 solutions has been refined :
Number of regular solutions : 8.
Number of singular solutions : 0.
Number of real solutions : 2.
Number of complex solutions : 6.
Number of clustered solutions : 0.
Number of failures : 0.
===========================================================================
The solution provided by triade my symbolic solver in ALDOR is
{z^2 +2*z -1,
y -z,
x -z}
{z,
y -1,
x}
{z,
y,
x -1}
{z -1,
y,
x}
Dimensions: [0,0,0,0]
Degrees: [2,1,1,1]
How to choose between symbolic and numeric methods?
 mathend000#
mathend000#- If the input is an approximate system, then only numeric
(or symbolic-numeric) methods make sense.
 mathend000#
mathend000#- If the input is an exact system but the user only cares
about approximate solutions, then symbolic-numeric
methods are more appropriate.
 mathend000#
mathend000#- If both the input and the desired answer are exact,
then only symbolic methods make sense. Examples:
- Computation of canonical forms (in order to recognize certain properties),
- Looking for real solutions (and discarding solutions with imaginary part)
- Computing modulo primes (cryptography, auto-correcting codes).


Next: A breif history
Up: Computer Algebra
Previous: Computer Algebra
Marc Moreno Maza
2007-01-10