|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
E 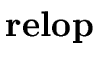 |
|
E |
|
E |
BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS are constructed using boolean operators. We will consider here the following rules.
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
E 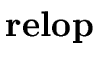 |
|
E |
|
E |
WHILE STATEMENTS WITH THE NUMERICAL METHOD.
| Production | Semantic Rule |
S 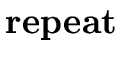 S1 S1 |
S.begin := newlabel |
| S.after := newlabel | |
| code1 := generate(S.begin ':') | | E.code | | | |
| code2 := generate('if ' E.place '= 0 ' 'goto' S.after) | | S1.code | |
| code3 := generate('goto' S.begin) | | generate(S.after) | |
| S.code := code1 | | code2 | | code3 |
FLOW OF CONTROL STATEMENTS WITH THE JUMP METHOD. We will consider here the following rules.
| S |
|
|
| S |
|
|
| S |
|
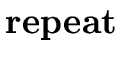 S1 S1 |
| Production | Semantic Rule |
|
S |
E.true := newlabel |
| E.false := S.next | |
| S1.next := S.next | |
| S.code := E.code | | generate(E.true ':') | | S1.code | |
|
S |
E.true := newlabel |
| E.false := newlabel | |
| S1.next := S.next | |
| S2.next := S.next | |
| code1 := E.code | | generate(E.true ':') | | S1.code | |
| code2 := generate('goto' S.next) | | | |
| code3 := generate(E.false ':') | | S2.code | |
| S.code := code1 | | code2 | | code3 | |
S 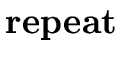 S1 S1 |
S.begin := newlabel |
| E.true := newlabel | |
| E.false := S.next | |
| S1.next := S.begin | |
| code1 := generate(S.begin ':') | | E.code | |
| code2 := generate(E.true ':') | | S1.code | |
| code3 := generate('goto' S.begin) | |
| S.code := code1 | | code2 | | code3 |
TRANSLATION OF BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS WITH THE JUMP METHOD. We will consider here the following rules.
| E |
|
E1 |
| E |
|
E1 |
| E |
|
|
| E |
|
(E1) |
| E |
|
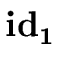 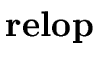 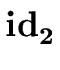 |
| E |
|
|
| E |
|
|
| Production | Semantic Rule |
|
E |
E1.true := E.true |
| E1.false := newlabel | |
| E2.true := E.true | |
| E2.false := E.false | |
| E.code := E1.code | | generate(E1.false':') | | E2.code | |
|
E |
E1.true := newlabel |
| E1.false := E.false | |
| E2.true := E.true | |
| E2.false := E.false | |
| E.code := E1.code | | generate(E1.true':') | | E2.code | |
|
E |
E1.true := E.false |
| E1.false := E.true | |
| E.code := E1.code | |
|
E |
E1.true := E.true |
| E1.false := E.false | |
| E.code := E1.code | |
E 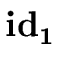 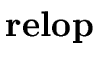 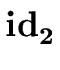 |
code1 := generate('if'
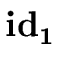 .place .place 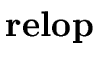 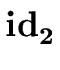 .place 'goto' E.true) .place 'goto' E.true) |
| code2 := generate('goto' E.false) | |
| E.code := code1 | | code2 | |
|
E |
E.code := generate('goto' E.true) |
|
E |
E.code := generate('goto' E.false) |
a < bAssume that
| if a < b goto Ltrue | |
| goto Lfalse | |
Observations.
a < b or c < dAgain assume that the labels Ltrue and Lfalse have been set for the entire expression. Then the translation is
| if a < b goto Ltrue | |
| goto L1 | |
| L1: | if c < d goto Ltrue |
| goto Lfalse | |
a < b or (c < d and e < f)Then the translation is
| if a < b goto Ltrue | |
| goto L1 | |
| L1: | if c < d goto L2 |
| goto Lfalse | |
| L2: | if e < f goto Ltrue |
| goto Lfalse | |
Of course the generated code is not optimal! Indeed the second statement can be eliminated.
while a < b do
if c < d then
x := y + z
else
x := y - z
Then the translation is
| L1: | if a < b goto L2 |
| goto Lnext | |
| L2: | if c < d goto L3 |
| goto L4 | |
| L3: | t1 := y + z |
| x := t1 | |
| goto L1 | |
| L4: | t2 := y - z |
| x := t2 | |
| goto L1 | |
| Lnext: | |