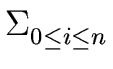 fixi be a univariate
polynomial over
fixi be a univariate
polynomial over
| f|2 = 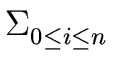 | fi|2 | fi|2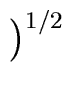 |
(72) |
where | z| denotes the square root of the product of z by its conjugate
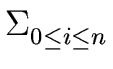 fixi be a univariate
polynomial over
fixi be a univariate
polynomial over
| f|2 = 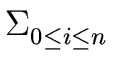 | fi|2 | fi|2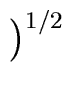 |
(72) |
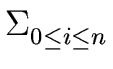 fixi
we shall compute a bound B such that for any
h
fixi
we shall compute a bound B such that for any
h | h | f |
(73) |
(2) -> factor(x^105 - 1)
(2)
2 4 3 2
(x - 1)(x + x + 1)(x + x + x + x + 1)
*
6 5 4 3 2
(x + x + x + x + x + x + 1)
*
8 7 5 4 3
(x - x + x - x + x - x + 1)
*
12 11 9 8 6 4 3
(x - x + x - x + x - x + x - x + 1)
*
24 23 19 18 17 16 14 13
x - x + x - x + x - x + x - x
12 11 10 8 7 6 5
+ x - x + x - x + x - x + x - x + 1
*
48 47 46 43 42 41 40
x + x + x - x - x - 2x - x
39 36 35 34 33
- x + x + x + x + x
32 31 28 26 24 22 20
+ x + x - x - x - x - x - x
17 16 15 14 13
+ x + x + x + x + x
12 9 8 7 6 5 2
+ x - x - x - 2x - x - x + x + x + 1
Type: Factored Polynomial Integer
Worse than that: for every B > 0 there exist infinitely many n such that
there exists a polynomial h dividing xn - 1 and satisfying
| h|2 > B.
See [vzGG99] for more details.
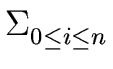 fixi and define
f-1 = fn+1 = 0.
We calculate
fixi and define
f-1 = fn+1 = 0.
We calculate
|
(75) |
![]()
f = 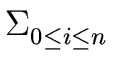 fixi = fn fixi = fn 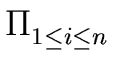 (x - zi) (x - zi) |
(76) |
We define the measure of the polynomial f by
M(f ) = | fn | 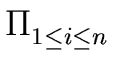 max(1, | zi | ) max(1, | zi | ) |
(77) |
| | z1 | ,..., | zk | > 1 and | zk+1 | ,..., | zn | |
(79) |
| M(f ) = | fn . z1 ... zk | | (80) |
|
(81) |
|
(82) |
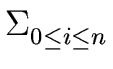 fixi
it is convenient to use the 1-norm
fixi
it is convenient to use the 1-norm
| f|1 = 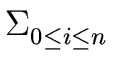 | fi | | fi | |
(83) |
| f|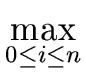 ( | fi | ) ( | fi | ) |
(84) |
| | f| |
(85) |
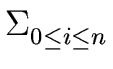 fixi and
h =
fixi and
h = 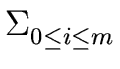 hixi
be two polynomials such that h divides f.
Then we have
hixi
be two polynomials such that h divides f.
Then we have
| h|2 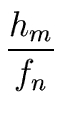 |
(86) |
h = hn 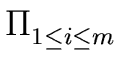 (x - ui) (x - ui) |
(87) |
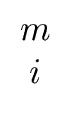
| hi | 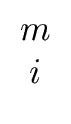 |
(88) |
| h|2 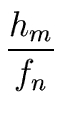 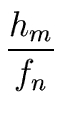 |
(91) |
| | g| |
(92) |
| | g|1 | h|1 |
(93) |
| | g|1 |
(94) |
| M(g) M(h) |
(95) |
| M(f ) |
(96) |
| | g|1 | h|1 |
(97) |
| | h| |
(98) |